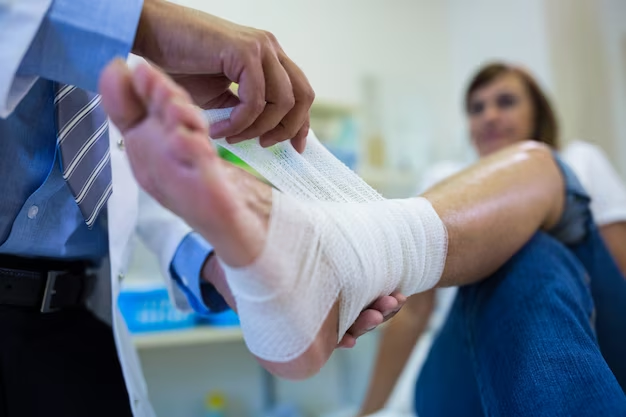
Treatment of Chronic & Acute Wound Infections by the Wound Care Centre in Ventura
When it comes to wound infections, there are two main types: acute wounds that occur suddenly and chronic wounds that persist over time.
Either way, the right treatment is crucial. When the wound is left untreated or not given proper treatment, it can get infected and worsen the healing process.
This article will provide practical insights on acute wounds vs. chronic wounds, their treatment options, and the path to recovery.
Different Stages of Wound Healing
Before you get into the different types of wound healing, it is significant to understand how your wounds progress through the healing process.
Wound healing is a complex, lengthy, and coordinated process that includes several stages.
These stages are as follows:
Stage 1: Hemostasis
This is the first stage of wound healing that starts immediately after an injury occurs on your skin.
Here, Hemostasis involves stopping the bleeding where the blood vessels will be constricted to reduce blood flow to the injured area and the blood clots.
The clot also provides a temporary barrier to pathogens, reducing the risk of infection.
People with different conditions, such as diabetes, venous insufficiency, thrombocytopenia, and other blood dyscrasias, can interfere clot formation. So, if an individual has these conditions, they have poor wound healing.
Stage 2: Inflammation
Once the clot is formed, your body will signal the cells around the injury to cause inflammation. So, it’s the next stage characterized by redness, heat, swelling, and pain at the wound site.
However, to heal the wound, your body appoints white blood cells, predominantly neutrophils and macrophages, to the wound.
These cells help remove debris, dead tissue, and potential pathogens.
Inflammation also plays a role in initiating the tissue repair process by releasing growth factors and other signaling molecules that stimulate cell migration and proliferation.
If you find the inflammation occurring too long, it’s time to change your treatment plan for chronic wound care. Visit the wound care center in Oxnard and get proper diagnosis and treatment.
Stage 3: Proliferation
Only when the inflammation starts to drop does proliferation occur. So, this stage begins a few days after the injury.
Here, new tissues called fibroblasts are formed, covering the injury and replacing the damaged or lost tissue. Since new growth factors are produced, different cells start multiplying more rapidly. This stage is also called the primary stage of wound healing.
Note that it’s highly essential to care for your wound during proliferation. Otherwise, there are chances for your wound to revert to the inflammation stage.
Stage 4: Remodeling
This is the last stage of wound healing that can last several months or even years after the initial injury. During this stage, collagen production at the injury starts to increase, so your tissues inside the wound undergo restructuring and strengthening and get closed completely.
These are the four different stages of wound healing. However, the wound’s healing speed and effectiveness can be influenced by multiple factors, including the person’s health condition, medical conditions, and the size and type of the wound.
Acute Wounds Vs Chronic Wounds
What is an acute wound?
An acute wound is an injury caused suddenly to your skin and its underlying tissues. Acute wounds follow the different stages of healing mentioned above. So, they have a predictable and orderly healing process that progresses through multiple stages.
These stages differ a bit for every individual based on some factors, like their health condition and the size and type of the wound. However, they will definitely heal over a short period of time without causing any significant complications.
Causes of an acute wound:
- Burns are caused by heat, cold, electricity, friction, chemicals, or radiation.
- Surgical wounds are incisions that are made by a healthcare professional purposefully. They cut your skin precisely, creating clean edges around the wound, and are closed using stitches, adhesive, or else left open to heal.
- Traumatic wounds are sudden injuries, such as a skinned knee, or something more severe, such as a gunshot wound. These injuries have deep lacerations, bites, skin tears, and penetrating trauma wounds.
What is a chronic wound?
Chronic wounds are wounds that don’t go through the normal phases of wound healing. They don’t follow any order or manner. They often stall in the inflammation phase, which is the second stage of wound healing.
Can an acute wound turn into a chronic wound?
Yes, if a wound fails to heal completely in two months, it can be considered a chronic wound. Also, if you simply have an acute wound and it doesn’t heal quickly or gets complicated, look for any signs or symptoms that indicate the transition into a chronic wound. The primary sign is irregular healing.
If the wound has any pus, extreme pain, or excessive inflammation throughout the healing process, it could be a sign that the acute wound has transitioned into a chronic wound.
Causes of chronic wounds
Some of the most common underlying causes of chronic wounds include:
- Diabetes
Diabetes patients have a 15% to 25% chance of developing a chronic wound. It’s because the blood vessels tend to become narrow and cause poor blood circulation. So, this causes poor circulation and limits the ability of red and white blood cells to travel to the wound sites.
- Venous and arterial ulcers
Venous ulcers result from damage to the leg vein due to conditions such as chronic venous insufficiency and varicose veins. Whereas, arterial ulcers are caused by reduced blood flow that leads to tissue death.
- Pressure ulcers
Formerly known as bedsores, these are skin injuries caused by prolonged pressure, friction, and moisture in areas with bony prominences like heels, ankles, coccyx, and hips.
- Other causes of chronic wounds:
Vascular Diseases (Peripheral Artery Disease)
Limited Mobility
Repeated Trauma to the Wound Site
Infection-Causing Bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus)
Edema (swelling)
To keep patients with chronic wounds safe, it’s important to use advanced wound dressings in conjunction with nutritional interventions and a wound care specialist.
Chronic & Acute Wound Infections Treatment by the Wound Care Centre in Ventura
How to treat an acute wound?
If it’s a small, acute wound, you can treat it at home. But if you aren’t confident enough, visit a wound care center and get it treated.
Follow these steps to treat an acute wound treatment:
- Wash your hands thoroughly using soap and water to reduce the risk of introducing more bacteria to your wound.
- Gather the necessary supplies, including antiseptic solution, clean water, disposable gloves, clean water, and adhesive strips or bandages.
- Examine your wound. Look for signs of infection, including swelling, increased pain and redness, pus or discharge, and warmth around the wound. If you suspect an infection, it’s always best to consult your doctor for guidance.
- If the wound is not too severe and doesn’t require any immediate medical attention, you can clean it gently.
Use clean, lukewarm water and mild soap to gently clean the wound. Avoid scrubbing, as this can damage tissue. Rinse the wound thoroughly to remove all soap residue.
Next, use a clean cloth or sterile gauge to pat the wound area dry. Avoid using cotton balls or tissue, as their fibers can stick to the wound.
- To avoid developing unnecessary infections, it’s best to apply an over-the-counter antiseptic solution to the wound as directed on the product label. This can help kill bacteria in the wound.
If your wound is deep or shows signs of infection, apply a thin layer of antibiotic ointment to the cleaned wound.
- After applying the medicine, cover the wound by placing a sterile dressing or adhesive bandage. Because keeping the wound dry is important to prevent further infection,
In most cases, your acute wounds will heal when cared for properly. But if you are careless about it, it can develop an infection and make the wound worse.
Treating an acute wound infection is critical to prevent the infection from spreading and to promote proper wound healing. If you doubt an infection, visit your doctor immediately.
Looking for a trusted wound care specialist in Thousand Oaks? Book an appointment and receive expert care for your wound healing needs.
How to Treat a Chronic Wound?
In the initial stage, treating a chronic wound is the same as treating an acute wound. But you must clean your chronic wound regularly and change the dressing to avoid infection.
Chronic wounds take a long time to heal, or they never heal. Some treatment options to cure these wounds with infections include:
Debridement
A wound care specialist would suggest the removal of dead or inflamed tissue. This process is called debridement. The patient is given a local anesthetic to ease the discomfort caused while removing the damaged tissue that interferes with the wound healing process.
Wound dressing
When the chronic wounds are cleaned, they are covered with a dressing. There are different kinds of dressings, including gauze, films, hydrogel dressings, foam dressings, and hydrocolloid dressings.
These dressings remove excess fluid from the wound and protect it from infection.
Compression stockings and compression bandages
If the chronic wound is caused by poor blood circulation, compression stockings or bandages are suggested. They can help the veins carry blood back to the heart and improve circulation.
Skin grafts
If the wound is large and struggling to close on its own, then skin grafts are done. This procedure involves skin taken from another part of the body, especially yours, and transplanted onto the wound.
Therapies
There are different therapy options available for treating chronic wounds. It includes hyperbaric oxygen therapy, ultrasound and electromagnetic therapy, and negative pressure wound therapy.
The chronic wounds reportedly cured within six months in
61 out of 100 people who underwent skin grafts
40 out of 100 people had wound dressings.
At Center for Advanced Wound Care in Los Angeles and Thousand Oaks, you wil find top-quality chronic wound care services. Visit us today and get your wound healed.
Final Words
Whether you are facing chronic or acute wound infections, timely and right treatment is essential for effective healing and preventing complications.
Are you dealing with acute or chronic wounds? Or are you not sure what kind of wound you are suffering from? Visit the Center for Advanced Wound Care in Thousand Oaks, which specializes in diagnosing and treating different wound types. Get in touch today and let your path to a speedy recovery begin.


